Difference between revisions of "Howto Zywall"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
# Select the "Use a virtual adapter and assigned address" method. Each client that connects to the gateway will need to have a unique virtual address manually configured. If more that one client connects to the gateway simultaneously using the same address, it will have conflicts and one of them will stop working unexpectedly. | # Select the "Use a virtual adapter and assigned address" method. Each client that connects to the gateway will need to have a unique virtual address manually configured. If more that one client connects to the gateway simultaneously using the same address, it will have conflicts and one of them will stop working unexpectedly. | ||
# Select the "Use an existing adapter and current address" option under the General tab. This also works with my Zywall but will has some severe limitations in a production environment ... | # Select the "Use an existing adapter and current address" option under the General tab. This also works with my Zywall but will has some severe limitations in a production environment ... | ||
| − | # Two clients cannot use the same public adapter address simultaneously when connecting to the Zywall gateway. This can happen easily if two clients exist behind different SOHO firewalls and receive the same address via DHCP. Essentially, this creates a similar problem to using option (1) and configuring identical virtual adapter address for more than one client. | + | #: a) Two clients cannot use the same public adapter address simultaneously when connecting to the Zywall gateway. This can happen easily if two clients exist behind different SOHO firewalls and receive the same address via DHCP. Essentially, this creates a similar problem to using option (1) and configuring identical virtual adapter address for more than one client. |
| − | # | + | #: b) The Zywall needs to be the default gateway for the network it protects or NAT all inbound IPsec traffic that passes to the private network. Otherwise, the return traffic destined to the client will go out your default gateway instead of being seen by the Zywall. |
| − | # | + | #: c) The client cannot use a public adapter address that exists in any private network protected by the Zywall. If this happens, you will end up with a very confused gateway that doesn't know which direction to pass the traffic. This can easily happen, again, if the client exists behind a SOHO firewall that uses an IP pool that maps to one of your internal networks. |
== Resources == | == Resources == | ||
| − | [ | + | [[Media:zywall.vpn.txt]] |
Latest revision as of 05:27, 9 January 2013
Contents
Introduction
This guide provides information that can be used to configure a Zywall device to support IPsec VPN client connectivity. The Shrew Soft VPN Client has been tested with Zywall products to ensure interoperability.
Overview
The configuration example described below will allow an IPsec VPN client to communicate with a single remote private network. No automatic configuration is possible at this time due to limitations in the Zywall firmware.
Gateway Configuration
This example assumes you have knowledge of the Zywall web configuration interface. For more information, please consult your Zywall product documentation.
Interfaces
Two network interfaces are configured. The WAN interface has a static public IP address of 10.1.1.23 which faces the internet. The LAN interface has a static private IP address of 10.1.2.23 which faces the internal private network. The default gateway is configured as 1.1.1.3 via the WAN interface.
Configuring VPN Rules
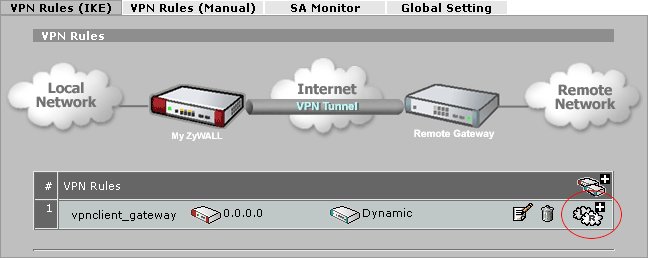
A Gateway Policy must be configured to define the IKE phase1 negotiation parameters. Navigate to the following screen using the pane on the left hand side of the browser interface.
Click on the following Add Gateway Icon + symbol on the right hand side of the VPN Rules header.
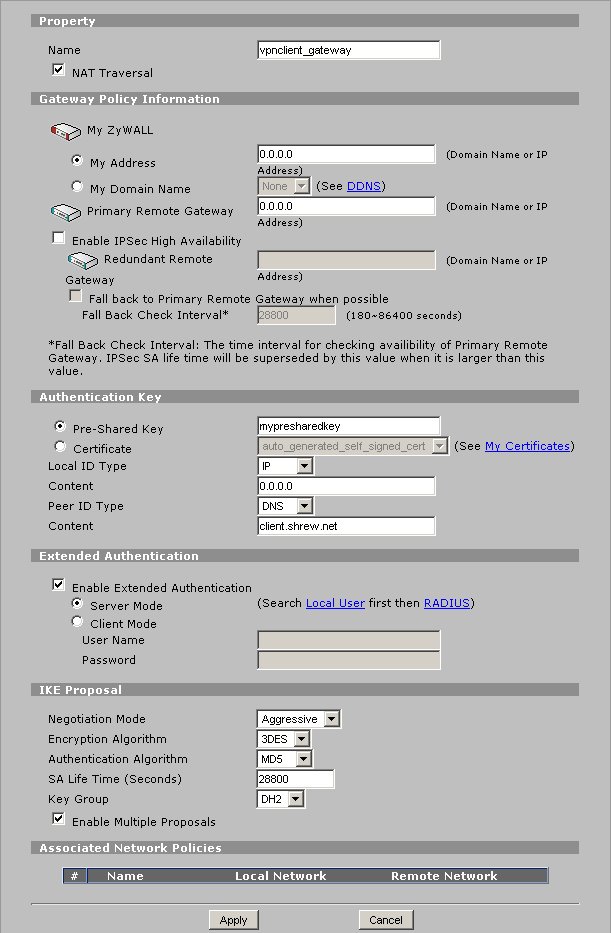
Define the following parameters.
- Property
- Name = vpnclient_gateway
- NAT Traversal = Checked
- Authentication Key
- Pre-Shared Key = mypresharedkey
- Local ID Type = IP
- Content = 0.0.0.0
- Peer ID Type = DNS
- Content = client.domain.com
- Extended Authentication = Checked
- Server Mode = Selected
When finished, click Apply.
Add a Network Policy
A Network Policy must be configured to define the IPsec policy and IKE phase2 negotiation parameters. Click on the following Add Network Policy Icon + symbol on the right hand side of the Gateway Policy row.
Define the following parameters.
- Property
- Active = Checked
- Name = vpnclient_policy1
- Gateway Policy Information
- Gateway Policy = vpnclient_gateway
- Local Network
- Address Type = Subnet Address
- Starting IP Address = 10.1.2.0
- Ending IP / Address Subnet = 255.255.255.0
- Local Port
- Start 0
- End 0
- Remote Network
- Address Type = Single Address
- Starting IP Address = 0.0.0.0
- Ending IP / Address Subnet = 0.0.0.0
- Remote Port
- Start 0
- End 0
- IPsec Proposal
- Encapsulation Mode = Tunnel
- Active Protocol = ESP
- Encryption Algorithm = 3DES
- Authentication Algorithm = MD5
- SA Life Time ( Seconds ) = 3600
- Perfect Forward Security = NONE
- Enable Replay Protection = Checked
- Enable Multiple Proposals = Checked
When finished, click Apply.
Configure Xauth User Accounts
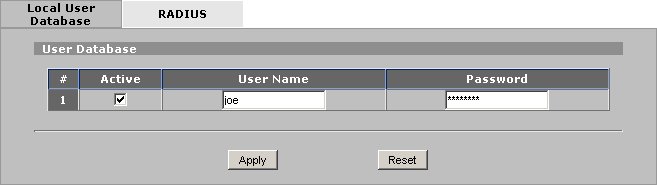
Xauth user accounts can be created locally on the Zywall appliance. Navigate to the following screen using the pane on the left hand side of the browser interface.
Define the following parameters for each remote access user.
- Active = Checked
- Username = [ user name ]
- Password = [ user password ]
When finished, click Apply.
Client Configuration
The client configuration in this example is less than ideal due to limitations of the Zywall. Open the Access Manager application and create a new site configuration. Configure the settings listed below in the following tabs.
General Tab
The Remote Host section must be configured. This Host Name or IP Address is defined as 10.1.2.23 to match the Zywall WAN interface address. The Auto Configuration option is set to disabled as Zywall does not support automatic client configuration.
Each remote access client must be assigned a unique Virtual Adapter IP address. Please see the known issues section of this document for more details. In this example we define an address of 10.2.23.2 with a netmask as 255.255.255.0 for a single client. Each subsequent client would be assigned the next address in the network. For example, the next is assigned 10.2.23.3, the next 10.2.23.4, etc ...
Phase 1 Tab
The Proposal section must be configured. The Exchange Type is set to aggressive and the DH Exchange is set to group 2 to match the Zywall Gateway Policy definition.
Authentication Tab
The client authentication settings must be configured. The Authentication Method is defined as Mutual PSK + XAuth.
Local Identity Tab
The Local Identity parameters are defined as Fully Qualified Domain Name with a FQDN String of "client.domain.com" to match the Zywall Gateway Policy definition.
Remote Identity Tab
The Remote Identity parameters are set to IP Address with the Use a discovered remote host address option checked to match the Zywall Gateway Policy definition.
Credentials Tab
The Credentials Pre Shared Key is defined as "mypresharedkey" to match the match the Zywall Gateway Policy definition.
Policy Tab
The IPsec Policy configuration must be manually configured when communicating with Zywall gateways. A single Topology Entry is defined to include the 10.1.2.0/24 network.
Known Issues
Building a client configuration for Zywall appliances can be problematic as they have no support for address assignment via modecfg. There are two options available to work around this shortcoming.
- Select the "Use a virtual adapter and assigned address" method. Each client that connects to the gateway will need to have a unique virtual address manually configured. If more that one client connects to the gateway simultaneously using the same address, it will have conflicts and one of them will stop working unexpectedly.
- Select the "Use an existing adapter and current address" option under the General tab. This also works with my Zywall but will has some severe limitations in a production environment ...
- a) Two clients cannot use the same public adapter address simultaneously when connecting to the Zywall gateway. This can happen easily if two clients exist behind different SOHO firewalls and receive the same address via DHCP. Essentially, this creates a similar problem to using option (1) and configuring identical virtual adapter address for more than one client.
- b) The Zywall needs to be the default gateway for the network it protects or NAT all inbound IPsec traffic that passes to the private network. Otherwise, the return traffic destined to the client will go out your default gateway instead of being seen by the Zywall.
- c) The client cannot use a public adapter address that exists in any private network protected by the Zywall. If this happens, you will end up with a very confused gateway that doesn't know which direction to pass the traffic. This can easily happen, again, if the client exists behind a SOHO firewall that uses an IP pool that maps to one of your internal networks.